When landing on Canadian territory, you find yourself immersed in a reality completely distinct from your own. No matter how much you have prepared, there is always more to learn and adapt to, from the nuances of local waste disposal to complexities such as the addition of 0.10 cents when purchasing a bottle of beverage.
Understanding the workings of a phone plan or renting a property often leads to an inevitable encounter with the concept of “credit score” or credit history in Canada. For a newcomer, establishing financial ties is essential to ensure a solid foundation for the future. However, building a credit history in a place where you are unknown and have no history can be a challenging task.
Thus, the journey to build credit in the country often requires providing guarantees to necessary companies, such as security deposits and upfront payments.
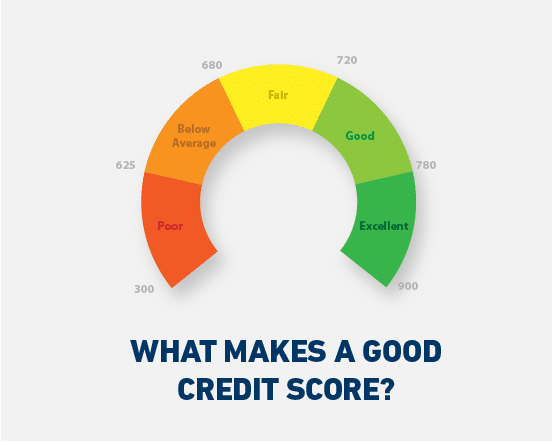
What is the credit score?
In summary, it is a score that reflects your financial behavior. These points are established when you acquire any form of credit, such as a credit card, a loan, or services with regular payments, such as a postpaid cell phone account or internet and cable TV services.
This score is a measure of the relationship between the amount of money borrowed or spent in advance and the readiness to repay these debts. Your credit score determines the level of risk you represent to lenders.
How is the score determined?
Similar to Serasa Experian in Brazil, Canada has two major credit agencies, Equifax and TransUnion. Every financial transaction made with the card or bill payments is reported to these agencies, which process the data and calculate the score.
What is the credit score used for?
The credit score represents the synthesis of your financial life in the country, resembling the system in the United States. It is used to determine the amount of money you can borrow, as a guarantee that you will fulfill agreements and payments, whether for the purchase of a car or a mortgage.
Credit card companies, banks, telephone companies, and property owners also check it to decide whether or not to grant you any service or product.
How to obtain a good score?
Given the whole context, you may be wondering how a newcomer to the country can acquire basic goods, since they do not have a financial history or score. There are several strategies to start this building, and it is crucial that planning begins as soon as the move to Canada is confirmed.
Bank account
The first step is to open a bank account in the country. Although Brazilian banks with a presence in Canada are scarce, it is possible to open a bank account while in Brazil, but it will be necessary to activate it in person upon arrival.
The most well-known banks include TD Canada Trust, Scotiabank, Bank of Montreal (BMO), HSBC, CIBC, and RBC Royal Bank. Generally, the required documents include a passport with a valid visa, proof of address, and a contact phone number. Many institutions do not require a minimum deposit and offer specific options for students.
Credit card
On the other hand, obtaining a credit card requires some additional steps for newcomers to Canada. Typically, you need to apply at a bank or institution that offers the service. Besides having credit, it is crucial to use it responsibly to build a solid history.
When applying for the card at the same institution where you opened the bank account, you will likely have two options. The card may have a low initial limit, which increases over time as you make purchases and timely payments, or you can leave a security deposit equivalent to the desired credit limit for a period of six months.
It is important to avoid having multiple credit cards, as this can negatively affect your score.
Healthy financial practices
Furthermore, it is essential to maintain healthy financial practices. Paying the full amount of bills on time is crucial to maintaining a good score. Constant delays in bill payments can negatively affect your history, resulting in unfavorable consequences. Asking for help is not a problem, and many banks can offer assistance in devising an appropriate financial plan.
How to check your score?
The score ranges from 300 to 900 and reflects your financial history. A score above 750 is considered excellent, while a score below 600 is seen as risky. Regularly checking your score can help identify possible errors and understand why an application may have been denied, allowing you to improve your financial habits. However, it is important to protect your personal and financial information from fraud.